
In a world filled with environmental pollutants and stress-inducing factors, our body’s defence mechanisms play a crucial role in maintaining our overall health and well-being. In this article, we will delve into the definition and significance of glutathione, as well as its potential glutathione benefits for your overall optimal health.
Glutathione, an influential antioxidant, is endogenously synthesized by the body’s cells. Its fundamental function lies in safeguarding cells against the harmful impact of oxidative stress and the consequent harm inflicted by free radicals. Glutathione is made up of three amino acids: cysteine, glutamate, and glycine. It is found in every cell of the body, but levels can vary depending on factors such as age, diet, and lifestyle.
The levels of glutathione in the cell of the body may also be reduced by a number of factors, these includes environmental toxins poor nutrition and stress.
Research has shown that glutathione has numerous benefits for overall health. It has been associated with enhanced immune system strength, heightened cognitive abilities, and decreased inflammation. Research has also demonstrated the anti-aging potential of glutathione, as it safeguards cellular health and prevents damage. Furthermore, studies have revealed that glutathione exhibits detoxifying properties, aiding in the elimination of detrimental toxins from the body. Glutathione serves as a vital nutrient that contributes to the promotion of overall health and well-being.
What is Glutathione?
Glutathione is a powerful antioxidant that is naturally produced in our bodies. It is made up of three amino acids: cysteine, glutamic acid, and glycine. This antioxidant is present in every cell of our body and is involved in many critical processes, making it a cornerstone of our overall health.
The Role of Glutathione in the Body
Glutathione is an essential component of the body’s defence system against oxidative stress. It helps to neutralize harmful free radicals and protect cells from damage. Glutathione also plays a vital role in the detoxification process by binding to toxins and eliminating them from the body. It is also vital in building and repairing tissue
Glutathione’s involvement extends beyond its antioxidant and detoxification roles, encompassing a multitude of other bodily processes. It helps to regulate the immune system, support DNA synthesis and repair, and promote healthy cell growth and division.
Why is Glutathione Important?
Glutathione earns the title of “master antioxidant” owing to its exceptional capacity to counteract free radicals and safeguard our cells against oxidative stress. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can cause damage to our cells and DNA, leading to various health issues. By scavenging these harmful molecules, glutathione acts as a shield against cellular damage.
How Glutathione Works as an Antioxidant
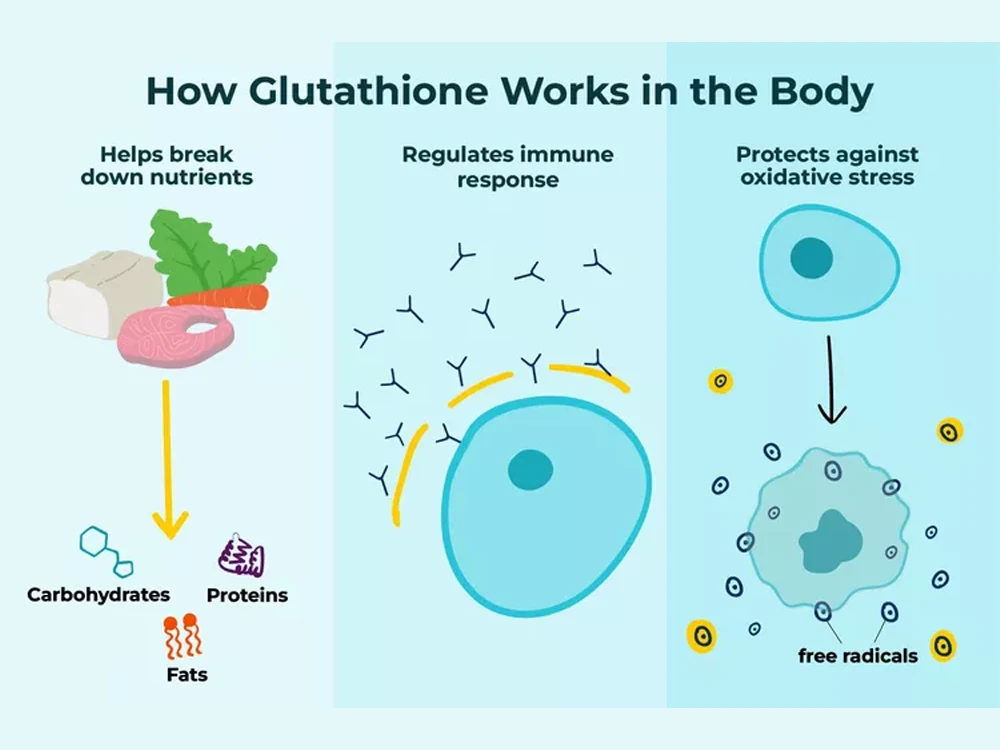
Glutathione works as an antioxidant by donating electrons to neutralize free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage cells and contribute to the development of many chronic diseases. Glutathione helps to prevent this damage by stabilizing free radicals and preventing them from causing harm.
Glutathione collaborates with additional antioxidants, like vitamin C and vitamin E, to deliver heightened safeguarding against oxidative stress. When these antioxidants neutralize free radicals, they become oxidized themselves. Glutathione helps to regenerate these antioxidants, allowing them to continue their protective functions.
Glutathione is an essential element of the body’s protective mechanism against oxidative stress and performs a critical function in numerous biological processes.
Benefits of Glutathione
Glutathione, an influential antioxidant, holds a pivotal position in upholding general well-being. It is a tripeptide molecule made up of three amino acids: cysteine, glutamine, and glycine. Glutathione is naturally produced in the body and is found in every cell.
1. Protection Against Free Radicals
As mentioned earlier, glutathione’s benefits primarly role is to combat free radicals. It acts as a potent antioxidant, intercepting and neutralizing these unstable molecules, thus preventing them from causing harm to our cells and tissues. This protection is crucial for maintaining optimal health and preventing oxidative damage [1].
2. Reducing Inflammation and Oxidative Stress
Inflammation and oxidative stress are two major contributors to many chronic diseases. Glutathione helps to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress by neutralizing free radicals and other harmful molecules. This, in turn, helps to protect cells from damage and may help to prevent the development of chronic diseases [2].
3. Boosts Immune System Function
Glutathione plays a vital role in supporting a robust immune system. It helps enhance the activity of immune cells, such as T cells and natural killer cells, which are responsible for fighting off infections and diseases [3]. By strengthening our immune response, glutathione promotes overall well-being and reduces the risk of illness.
Glutathione is essential for a healthy immune system. It helps to protect immune cells from damage caused by free radicals and other harmful substances. Glutathione additionally aids in modulating the immune response by regulating cytokine production, essential proteins involved in inflammation.
4. Supports Liver Detoxification
The liver is our body’s primary detoxification organ, responsible for breaking down harmful substances and eliminating them from our system. Glutathione plays a crucial role in this process by binding to toxins and aiding their removal from the liver. By supporting liver detoxification, glutathione helps maintain a healthy liver and promotes optimal functioning [4].
Glutathione is a key player in the body’s detoxification process. It helps to bind to and remove harmful toxins and heavy metals, such as mercury and lead. Glutathione also helps to support the liver, which is the body’s primary organ of detoxification.
5. Enhances Brain Health
Glutathione is essential for maintaining proper brain function and protecting against neurological disorders. It acts as a defence against oxidative stress in the brain, which can contribute to conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and other age-related cognitive decline. By reducing oxidative damage, glutathione supports brain health and promotes cognitive well-being [5].
6. Supports Heart Health
A healthy cardiovascular system is vital for overall well-being, and glutathione can contribute to its maintenance. Oxidative stress can cause damage to the cells lining our blood vessels, leading to atherosclerosis and heart disease. Glutathione assists in minimizing oxidative stress, thereby promoting heart health and lowering the likelihood of cardiovascular issues. [6][7].
7. Promotes Skin Health
Glutathione also plays a role in maintaining healthy skin. It helps protect our skin cells from damage caused by free radicals and supports the regeneration of healthy skin tissues. Glutathione has been associated with diminishing the visibility of age spots, wrinkles, and other indications of skin aging, resulting in a youthful and glowing complexion [8].
Glutathione has demonstrated beneficial effects on skin well-being. It aids in diminishing melanin production, which can contribute to hyperpigmentation and age spots. Additionally, glutathione safeguards skin cells against harm caused by UV radiation and other detrimental substances.
8. Improves Psoriasis
Psoriasis is an enduring skin condition distinguished by red, flaky patches. Glutathione has exhibited encouraging outcomes in lessening the intensity of psoriasis manifestations, aiding in enhancing skin well-being and quality of life [9].
9. Improves Insulin Resistance in Older People
Insulin resistance can lead to various health issues, especially in older individuals. Glutathione supplementation has been found to enhance insulin sensitivity, potentially reducing the risk of metabolic disorders.
10. Reduces Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects movement. Glutathione has shown promise in reducing oxidative stress and potentially alleviating symptoms associated with Parkinson’s disease [10].
11. Potential Benefits for Autism and Autoimmune Diseases
Glutathione has been explored for its potential role in supporting individuals with autism spectrum disorders and autoimmune conditions. Although further research is needed, preliminary studies suggest its beneficial effects [11][12].
12. May Help Peripheral Artery Disease:
Peripheral artery disease is characterized by reduced blood flow to the limbs. Glutathione’s antioxidant properties may contribute to improving blood circulation and mitigating symptoms associated with this condition [13].
Other benefits
- Improving sleep
- Boosting energy levels
- Reducing the risk of cancer
Sources of Glutathione
Dietary Sources
Glutathione is a naturally occurring antioxidant that is produced by the liver. It is also found in some foods, including:
- Fresh fruits, vegetables and whole grains, especially those that are high in vitamin C and sulfur-containing amino acids, such as broccoli, cauliflower, kale, Brussels sprouts, spinach, tomatoes, avocados, nuts and seeds.
- Fish, especially those that are high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon and tuna.
- Meat, especially red meat, which contains high levels of glutathione precursors.
However, it is important to note that cooking and processing can significantly reduce the glutathione content of foods. Therefore, it is recommended to consume these foods raw or lightly cooked to maximize their glutathione content.
Supplements
Glutathione supplements are also available in various forms, including:
- Oral supplements, which are available in capsules, tablets, and powders. However, oral supplements are not well absorbed by the body and may not be effective in raising glutathione levels.
- Intravenous (IV) glutathione, which is administered directly into the bloodstream. IV glutathione is more effective in raising glutathione levels than oral supplements, but it requires a healthcare professional to administer.
- Topical creams and lotions, which are applied directly to the skin. However, the effectiveness of topical glutathione in raising glutathione levels is still unclear.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any glutathione supplements, as they may interact with other medications or have potential side effects.
How to Increase Glutathione Levels
Now that we understand the remarkable benefits and sources of glutathione, let’s explore some effective ways to increase its levels in our bodies:
Lifestyle Changes
There are several lifestyle changes one can make to increase glutathione levels. These changes include:
- Exercising regularly, as exercise has been shown to increase glutathione levels.
- Eating a Healthy Diet: Consuming foods rich in glutathione precursors, such as sulfur-containing vegetables (broccoli, cauliflower, garlic, kale, onions) and fruits (avocado, watermelon), can help boost your glutathione levels naturally.
- Getting Enough Sleep: Prioritizing quality sleep allows your body to recharge and produce optimal levels of glutathione. Aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night. As glutathione levels are naturally replenished during sleep.
- Reducing Stress: Chronic stress can deplete glutathione levels. Incorporating stress management techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or engaging in hobbies, can help reduce stress and support glutathione production.
Supplements
- Taking Supplements: Glutathione supplements are available in various forms, including capsules, powders, and intravenous injections. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation.
In addition to lifestyle changes, there are also several supplements that can help increase glutathione levels. These supplements include:
- N-acetylcysteine (NAC), which is a precursor to glutathione and has been shown to increase glutathione levels in the body.
- Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA), which is an antioxidant that can help regenerate glutathione in the body.
- Milk thistle, which contains a compound called silymarin that can help increase glutathione levels.
It’s worth mentioning that although these supplements might assist in boosting glutathione levels, they should not be solely relied upon for increasing glutathione levels. Lifestyle changes, such as those mentioned above, should also be implemented for optimal results.
Increasing glutathione levels can have numerous health benefits, including improved immune function, reduced inflammation, and increased detoxification. By making simple lifestyle changes and incorporating certain supplements, individuals can naturally boost their glutathione levels and improve their overall health.
A solution? Cellgevity

Awaken your cells and Live healthier.
Precaution
Glutathione supplements are considered safe for general use; however, caution should be exercised during pregnancy and breastfeeding due to insufficient data on its safety in these conditions. It is advisable to avoid using glutathione supplements if you are pregnant or nursing. It is always important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplementation regimen to ensure the best course of action for your specific situation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, glutathione is a powerful antioxidant that plays a critical role in overall health. From its role in protecting against free radicals to supporting immune function, liver detoxification, brain health, heart health, cellular repair, and skin health, glutathione is truly a superstar molecule.
While the body naturally produces glutathione, certain factors such as aging, stress, and poor diet can lead to a decrease in levels. Supplementing with glutathione or its precursors may offer benefits for those with certain health conditions or those looking to improve their overall health.
However, it is important to note that more research is needed to fully understand the potential benefits and risks of glutathione supplementation. It is also important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Incorporating glutathione-rich foods into one’s diet and living a preventive healthy lifestyle may be the best way to support the body’s natural production of this important antioxidant and reap the rewards of enhanced well-being.
Remember, the key to unlocking the full potential of glutathione lies in understanding its benefits and implementing strategies to increase its levels. So, take the necessary steps today to harness the power of this remarkable antioxidant and experience the positive impact it can have on your overall health and vitality.
Frequently Asked Question
Here are the answers to your questions about glutathione:
What happens when you start taking glutathione?
When you start taking glutathione, you may experience a number of benefits, including:
- Improved skin health
- Increased energy levels
- Reduced inflammation
- Improved immune function
- Reduced risk of chronic diseases
Is glutathione the most powerful antioxidant?
Glutathione is one of the most powerful antioxidants in the body. It helps to protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage cells and lead to a number of health problems, including cancer, heart disease, and Alzheimer’s disease.
Why is glutathione called the mother of all antioxidants?
Glutathione is called the mother of all antioxidants because it helps to regenerate other antioxidants, such as vitamin C and vitamin E. This makes glutathione even more effective at protecting cells from damage.
Does glutathione affect kidney?
Glutathione is important for kidney health. It helps to protect the kidneys from damage caused by toxins and free radicals. Glutathione also helps to remove toxins from the body through the kidneys.
What to avoid when taking glutathione?
There are a few things to avoid when taking glutathione, including:
- Alcohol
- Smoking
- Certain medications, such as chemotherapy drugs and anti-psychotic drugs
Can glutathione cleanse the liver?
Glutathione is a powerful detoxifier that can help to cleanse the liver. It helps to remove toxins from the liver and improve liver function.
Who should avoid glutathione?
People who should avoid glutathione include:
- People who are pregnant or breastfeeding
- People with autoimmune diseases
- People with liver disease
What disease is associated with glutathione?
Glutathione deficiency has been linked to a number of diseases, including:
- Cancer
- Heart disease
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Parkinson’s disease
- Autoimmune diseases
Why take vitamin C with glutathione?
Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that works synergistically with glutathione. Vitamin C helps to regenerate glutathione, making it even more effective at protecting cells from damage.
Does glutathione cleanse blood?
Glutathione is a powerful detoxifier that can help to cleanse the blood. It helps to remove toxins from the blood and improve blood circulation.
How long will it take for glutathione to work?
The time it takes for glutathione to work varies from person to person. Some people may start to see benefits within a few weeks, while others may need to take glutathione for several months to see results.
Does glutathione detox liver and kidneys?
Glutathione is a powerful detoxifier that can help to cleanse the liver and kidneys. It helps to remove toxins from these organs and improve their function.
Sources
At Glutathione360, we strive to provide accurate and relevant information about glutathione. Our articles are backed by verified information from reputable sources such as peer-reviewed research papers, academic research institutions, reputed organizations, and medical associations. We maintain a stringent editorial policy to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the content we present to our readers.
- Pizzorno J. Glutathione! Integr Med (Encinitas). 2014 Feb;13(1):8-12. PMID: 26770075; PMCID: PMC4684116.
- Ahn E, Lee J, Han J, Lee SM, Kwon KS, Hwang GS. Glutathione is an aging-related metabolic signature in the mouse kidney. Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Sep 7;13(17):21009-21028. doi: 10.18632/aging.203509. Epub 2021 Sep 7. PMID: 34492635; PMCID: PMC8457589.
- Prussick R, Prussick L, Gutman J. Psoriasis Improvement in Patients Using Glutathione-enhancing, Nondenatured Whey Protein Isolate: A Pilot Study. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2013 Oct;6(10):23-6. PMID: 24155989; PMCID: PMC3805302.
- Labarrere CA, Kassab GS. Glutathione: A Samsonian life-sustaining small molecule that protects against oxidative stress, ageing and damaging inflammation. Front Nutr. 2022 Nov 1;9:1007816. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1007816. PMID: 36386929; PMCID: PMC9664149.
- Ferreira AV, Koeken VACM, Matzaraki V, Kostidis S, Alarcon-Barrera JC, de Bree LCJ, Moorlag SJCFM, Mourits VP, Novakovic B, Giera MA, Netea MG, Domínguez-Andrés J. Glutathione Metabolism Contributes to the Induction of Trained Immunity. Cells. 2021 Apr 21;10(5):971. doi: 10.3390/cells10050971. PMID: 33919212; PMCID: PMC8143087.
- Jiang X, Du B, Zheng J. Glutathione-mediated biotransformation in the liver modulates nanoparticle transport. Nat Nanotechnol. 2019 Sep;14(9):874-882. doi: 10.1038/s41565-019-0499-6. Epub 2019 Jul 15. PMID: 31308501; PMCID: PMC7252432.
- Iskusnykh IY, Zakharova AA, Pathak D. Glutathione in Brain Disorders and Aging. Molecules. 2022 Jan 5;27(1):324. doi: 10.3390/molecules27010324. PMID: 35011559; PMCID: PMC8746815.
- Ghosh S, Sulistyoningrum DC, Glier MB, Verchere CB, Devlin AM. Altered glutathione homeostasis in heart augments cardiac lipotoxicity associated with diet-induced obesity in mice. J Biol Chem. 2011 Dec 9;286(49):42483-42493. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.304592. Epub 2011 Oct 23. PMID: 22021075; PMCID: PMC3234958.
- Jawaid S, Strainic JP, Kim J, Ford MR, Thrane L, Karunamuni GH, Sheehan MM, Chowdhury A, Gillespie CA, Rollins AM, Jenkins MW, Watanabe M, Ford SM. Glutathione Protects the Developing Heart from Defects and Global DNA Hypomethylation Induced by Prenatal Alcohol Exposure. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2021 Jan;45(1):69-78. doi: 10.1111/acer.14511. Epub 2021 Jan 2. PMID: 33206417; PMCID: PMC8865806.
- Telorack M, Meyer M, Ingold I, Conrad M, Bloch W, Werner S. A Glutathione-Nrf2-Thioredoxin Cross-Talk Ensures Keratinocyte Survival and Efficient Wound Repair. PLoS Genet. 2016 Jan 25;12(1):e1005800. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005800. PMID: 26808544; PMCID: PMC4726503.
- Prussick R, Prussick L, Gutman J. Psoriasis Improvement in Patients Using Glutathione-enhancing, Nondenatured Whey Protein Isolate: A Pilot Study. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2013 Oct;6(10):23-6. PMID: 24155989; PMCID: PMC3805302.
- Effect of Glutathione Infusion on Leg Arterial Circulation, Cutaneous Microcirculation, and Pain-Free Walking Distance in Patients With Peripheral Obstructive Arterial Disease: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial Enrico Arosio, MD, Sergio De Marchi, MD, Massimo Zannoni, MD, Manlio Prior, MD, Alessandro Lechi, MD DOI:https://doi.org/10.4065/77.8.754
- Perricone C, De Carolis C, Perricone R. Glutathione: a key player in autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev. 2009 Jul;8(8):697-701. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2009.02.020. Epub 2009 Feb 13. PMID: 19393193.
- Rose S, Melnyk S, Pavliv O, Bai S, Nick TG, Frye RE, James SJ. Evidence of oxidative damage and inflammation associated with low glutathione redox status in the autism brain. Transl Psychiatry. 2012 Jul 10;2(7):e134. doi: 10.1038/tp.2012.61. PMID: 22781167; PMCID: PMC3410618.



